Are you curious about the science behind hair restoration and how modern treatments can bring back your natural hair? Many people struggle with hair loss, and understanding the secrets behind effective hair restoration methods can be life-changing. Have you ever wondered what really works and what’s just a myth? In this article, we will dive deep into the latest hair restoration techniques, revealing the cutting-edge science that makes them successful. From innovative hair transplant procedures to advanced non-surgical hair regrowth treatments, the options are more promising than ever before. But how do these treatments actually stimulate hair growth? What role do stem cells and growth factors play? You’ll find surprising answers that experts rarely share openly. Whether you’re battling thinning hair or searching for preventive solutions, knowing the scientific principles behind hair restoration can empower you to make informed choices. We’ll explore trending topics like PRP therapy for hair loss, laser hair growth technology, and the impact of nutrition on scalp health. Ready to uncover the secrets that could transform your hair and confidence? Keep reading to unlock the mysteries of hair restoration science and find out which methods are truly worth your attention!
How Does Hair Restoration Work? Unveiling the Latest Scientific Breakthroughs in Hair Regrowth
Hair loss is something that affects millions of people around the world, and in places like New York, the demand for effective hair restoration treatments has never been higher. But many still wonder, how does hair restoration work? What really behind the science of hair regrowth? This article will dive deep into the latest scientific breakthroughs, explain the fundamental mechanisms, and reveal some secrets of hair restoration that not many people know about.
What Is Hair Restoration Exactly?
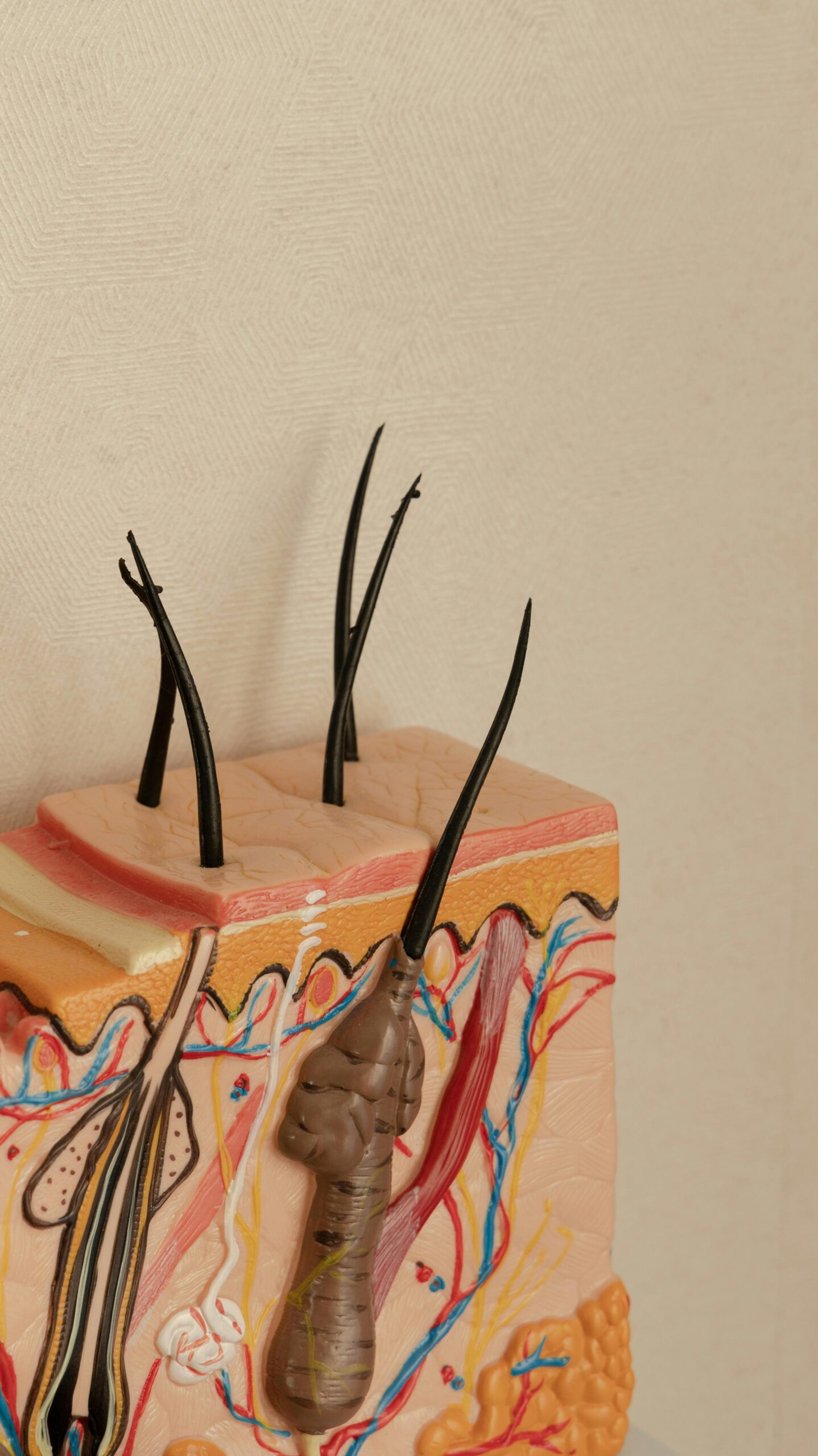
Hair restoration, simply put, is the process of regrowing hair or transplanting hair follicles to areas where hair has thinned or disappeared. It is not just about cosmetic fixes — it involves complex biological processes and medical techniques that aim to restore hair growth in a natural way.
Historically, people used wigs or topical oils, but modern hair restoration has advanced much beyond that. The evolution started from basic hair transplants in the 1950s, where doctors moved hair from one scalp part to another. Since then, innovations like Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy emerged to improve results and reduce side effects.
The Science Behind Hair Loss and Regrowth
To understand how hair restoration works, you gotta first understand why hair loss happens. Hair follicles go through cycles:
- Anagen (growth phase): Lasts 2-7 years, hair grows actively.
- Catagen (transitional phase): Lasts 2-3 weeks, hair stops growing.
- Telogen (resting phase): Lasts around 3 months, hair falls out and new hair starts to grow.
In hair loss conditions like androgenetic alopecia (male/female pattern baldness), this cycle gets disrupted. Hair follicles shrink and produce thinner, shorter hair strands until they stop producing hair altogether.
How Modern Hair Restoration Treatments Work
Different methods target different causes of hair loss. Here are some popular ones used in the clinics of New York:
Hair Transplant Surgery
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): A strip of scalp is removed, and individual follicular units are transplanted.
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Individual hair follicles are extracted and implanted on bald areas.
Both methods relocate healthy hair follicles to balding spots, allowing natural growth over time.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- Blood is drawn from the patient and spun in a centrifuge to concentrate platelets.
- Platelet-rich plasma is injected into scalp areas to stimulate hair follicles.
PRP contains growth factors that promote cell regeneration and improve hair follicle function.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
- Uses red light lasers to stimulate hair follicles.
- Enhances blood flow and cellular activity in scalp.
Medications
- Finasteride and Minoxidil are FDA-approved drugs.
- Finasteride blocks DHT hormone which causes follicle shrinkage.
- Minoxidil promotes blood flow and prolongs hair growth phase.
Latest Scientific Breakthroughs in Hair Regrowth
Science is constantly moving forward, and hair restoration is one of those fields where new discoveries appear frequently. Some of the most promising breakthroughs include:
Stem Cell Therapy: Researchers are working on extracting hair follicle stem cells and expanding them outside the body before implanting them back. This could potentially regenerate new follicles and reverse baldness.
3D Bioprinting: Scientists experimenting with printing hair follicles using bio-inks that mimic natural tissue. This futuristic approach could one day allow for unlimited hair follicle production.
Wnt Signaling Pathway Modulation: Wnt signaling controls hair follicle growth and development. New drugs aiming to activate this pathway are showing promising results in clinical trials.
Gene Editing Technologies: Using CRISPR to edit genes responsible for hair loss could provide permanent solutions in the future.
Comparing Hair Restoration Methods
It can be confusing to choose right treatment, so here’s a simple comparison:
| Treatment Type | Procedure | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| FUT (Strip Surgery) | Removal of scalp strip | High number of grafts | Longer scar, recovery time |
| FUE | Individual follicle extraction | Less scarring, quicker healing | More expensive, time-consuming |
| PRP | Injection of platelet-rich plasma | Non-surgical, boosts growth | Results vary, multiple sessions needed |
| LLLT | Laser light application | Painless, easy to use at home | Limited evidence, slow effects |
| Medications | Topical or oral drugs | Easy to use, accessible | Side effects, requires continuous use |
Practical Tips for Those Considering Hair Restoration in New York
- Consult a Specialist: Hair restoration is highly individualized. Only a
Top 5 Proven Hair Restoration Techniques Backed by Cutting-Edge Research
Hair loss, it’s something that affects millions worldwide, and finding the right treatment can be confusing, to say the least. Luckily, science has been working hard on understanding hair restoration, revealing some pretty exciting techniques that actually work. If you ever wonder what really behind hair restoration and what are the proven methods, you’re in the right place. This article dives into the top 5 hair restoration techniques backed by cutting-edge research, and also unpack the science behind how these treatments actually bring hair back to life.
The Science Behind Hair Restoration Explained: Secrets Revealed
Hair loss, medically called alopecia, often caused by genetics, hormones, aging, or sometimes medical conditions. But how hair restoration works? It all starts on a microscopic level with hair follicles, those tiny organs in your skin that grow hair. When hair loss happens, follicles shrink or stop producing hair. Modern science focus on either reviving these follicles or replacing them entirely.
Hair follicles go through cycles: growth (anagen), rest (telogen), and shedding (catagen). Restoring hair means either stimulating follicles stuck in resting phase or replacing lost follicles with new ones. This is why some treatments work better for certain types of hair loss than others.
Top 5 Proven Hair Restoration Techniques Backed by Cutting-Edge Research
Here’s a list of the most effective hair restoration techniques based on recent studies and clinical results. These methods have been tested in labs and clinics, showing promising results for many patients.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- What it is: A minimally invasive hair transplant where individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor area (usually back of the scalp) and implanted into thinning or balding areas.
- Why it works: Because it transplants healthy follicles directly, FUE can permanently restore hair growth.
- Research backs it: Studies show high graft survival rates (up to 95%) and natural-looking hairlines.
- Practical example: Someone with male pattern baldness can regain dense hair with almost no visible scarring.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- What it is: Blood is drawn from patient, processed to concentrate platelets, then injected into scalp.
- Why it works: Platelets release growth factors that stimulate dormant follicles to grow.
- Research backs it: Clinical trials report improved hair density and thickness after several sessions.
- Practical example: A woman with thinning hair sees noticeable improvement after 3 monthly treatments.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
- What it is: Non-invasive treatment using red light lasers to stimulate hair follicles.
- Why it works: Laser light improve blood flow and cellular metabolism in follicles.
- Research backs it: Multiple randomized controlled trials confirm increased hair count and thickness.
- Practical example: Men and women using laser caps or combs at home report slowed hair loss and new growth.
Minoxidil (Topical Solution)
- What it is: An FDA-approved topical medicine applied to scalp twice daily.
- Why it works: Minoxidil boosts blood circulation and prolongs hair follicle growth phase.
- Research backs it: Decades of clinical use shows it effective for androgenetic alopecia.
- Practical example: Younger patients with early hair thinning often see best results.
Hair Cloning and Stem Cell Therapy (Experimental but Promising)
- What it is: Lab-grown hair follicles from stem cells injected or implanted into scalp.
- Why it works: Potential to produce unlimited donor hair, overcoming limitations of traditional transplants.
- Research backs it: Still in clinical trials but early results are promising.
- Practical example: Future patients might see full scalp restoration without surgery.
Historical Context: How Hair Restoration Has Evolved
Hair restoration isn’t new, but the techniques had been crude for many years. Early attempts in mid-20th century involved large grafts called “hair plugs” which often looked unnatural. Over time, doctors developed smaller grafts and follicular units improving aesthetics dramatically.
In 1990s, FUE emerged as a game-changer, offering less scarring and quicker recovery. Around same time, topical treatments like minoxidil became widely used. PRP and laser therapies are more recent, becoming popular as non-surgical options.
Stem cell therapies represent the future, with research accelerating thanks to advances in regenerative medicine.
Comparison Table: Main Hair Restoration Techniques
| Technique | Invasiveness | Recovery Time | Effectiveness | Suitability | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) | Moderate | 1-2 weeks | High (permanent) | Male/female pattern baldness | $$$$ |
Exploring the Role of Stem Cells and PRP Therapy in Effective Hair Restoration
Hair loss is something many people face, and finding the right treatment is not always easy. In New York, hair transplant clinics are seeing a rise in interest for advanced therapies like stem cells and PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy. But what exactly is the science behind these treatments? How they work, and why are they becoming popular options for effective hair restoration? Let’s dive deep into the secrets behind hair restoration, and explore the role that stem cells and PRP therapy play in making hair grow back thicker and healthier.
The Science Behind Hair Restoration Explained
Hair restoration isn’t just about transplanting hair follicles from one part of the scalp to another. There’s a lot more happening at the cellular and molecular level. The hair follicle is a complex mini-organ that goes through cycles of growth (anagen), rest (telogen), and shedding (catagen). When hair loss occurs, it is often because the follicles shrink or because the growth phase shortens.
Scientists and doctors studied these processes and found ways to intervene using the body’s own healing mechanisms. This is where stem cells and PRP come into play.
What Are Stem Cells and How Do They Help Hair Growth?
Stem cells are special cells that can develop into many different types of cells in the body. In the context of hair restoration, two types of stem cells are important:
- Hair follicle stem cells: Located in the bulge area of the follicle, responsible for regenerating new hair.
- Mesenchymal stem cells: Found in fat tissue, can help by secreting growth factors that promote healing and growth.
In hair restoration, stem cell therapy involves harvesting these cells from a patient’s own body (usually from fat or scalp tissue), processing them, and injecting them back into the scalp. The goal is to reactivate dormant follicles and improve the scalp environment to support new hair growth.
PRP Therapy: What Is It and Why It Works
PRP therapy uses the patient’s own blood to help stimulate hair growth. The process includes drawing blood, spinning it in a centrifuge to separate the platelet-rich plasma, and then injecting this plasma into the scalp.
Platelets contain growth factors which are vital for healing and tissue regeneration. When injected into the scalp, PRP can:
- Increase blood supply to hair follicles
- Stimulate follicle stem cells
- Prolong the growth phase of hair
Because PRP uses the patient’s own biological material, it’s considered safe with minimal risks.
A Brief History of Hair Restoration Techniques
Hair restoration has evolved a lot over the last century. Here’s a quick look at how treatments progressed:
- 1930s-1950s: Early hair transplant attempts involved large plugs of hair, often looking unnatural.
- 1980s: Introduction of follicular unit transplantation (FUT), allowing more natural results.
- 2000s: Development of follicular unit extraction (FUE), a less invasive method.
- 2010s onwards: Use of regenerative medicine approaches like stem cells and PRP therapy.
This history shows a clear trend — from mechanical relocation of hair to biological stimulation of natural growth.
Stem Cell Therapy vs. PRP Therapy: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Stem Cell Therapy | PRP Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Patient’s own fat or scalp tissue | Patient’s own blood |
| Main Action | Reactivates dormant follicles, regenerates tissue | Stimulates blood flow and growth factors |
| Procedure Duration | Usually longer due to harvesting and processing | Shorter, typically 30-60 minutes |
| Number of Sessions | Fewer sessions needed but can be expensive | Multiple sessions often recommended |
| Risk | Minimal, but more invasive than PRP therapy | Very low, minimally invasive |
| Effectiveness | Potentially longer-lasting results | Effective for mild to moderate hair thinning |
Practical Examples: Who Can Benefit from These Treatments?
- Early-stage hair loss patients who want to avoid surgery might try PRP therapy first.
- Individuals with thinning hair but healthy scalp tissue often see good results from PRP.
- Those with more advanced hair loss may consider stem cell therapy combined with hair transplantation for best outcomes.
- People not suitable for traditional transplants (due to insufficient donor hair) might still benefit from regenerative treatments.
Additional Factors Influencing Hair Restoration Success
It’s important to remember that stem cells and PRP are not magic bullets. Several other factors play a role in determining how well these treatments work:
- Patient’s age and overall health
- Severity and cause of hair loss (genetic, hormonal, stress-related)
- Nutritional status and lifestyle habits (smoking, diet)
- Consistency with follow-up treatments and
What Causes Hair Loss? Understanding the Science to Choose the Best Restoration Method
What Causes Hair Loss? Understanding the Science to Choose the Best Restoration Method
Hair loss is a problem that many people in New York and around the world face every day. It can affect self-esteem and confidence, but surprisingly, many don’t really know what causes hair loss or how the science behind hair restoration works. Understanding these basics helps you to pick the best treatment for your situation. Let’s dive into the mysteries of hair loss and the science behind hair restoration, revealing secrets that often stay hidden until you visit a clinic.
Why Does Hair Fall Out? The Basics
Hair loss, scientifically known as alopecia, isn’t just one single condition — it has many causes and forms. The most common type is androgenetic alopecia, often called male or female pattern baldness. This form affects millions and is caused mostly by genetics and hormones. But there are other reasons too:
- Genetics: If your parents or grandparents had hair loss, chances are you might too. It runs in families because of certain genes that affect hair follicles.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormones like dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can shrink hair follicles, making hair thinner and shorter until it stops growing altogether.
- Medical Conditions: Issues like thyroid problems, autoimmune diseases (like alopecia areata), and scalp infections can lead to hair loss.
- Stress and Lifestyle: High stress levels, poor diet, and lack of sleep can trigger temporary hair loss.
- Medications and Treatments: Some drugs, like chemotherapy medicines, cause hair to fall out as a side effect.
The hair growth cycle itself is a key to understanding loss. Hair follicles go through phases:
- Anagen (growth phase): Can last 2-7 years.
- Catagen (transitional phase): About 2-3 weeks.
- Telogen (resting phase): Lasts around 3 months, after which hair falls out.
When this cycle gets disrupted, hair falls out faster than it grows back, causing thinning or bald spots.
The Science Behind Hair Restoration Explained
Hair restoration is not magic; it’s science carefully applied. This field has evolved a lot over decades, combining biology, surgery, and technology to help people regain hair naturally.
Historically, hair restoration started with hair plugs in the mid-20th century — these were large, unnatural clumps of hair transplanted to bald areas. Today, the methods are advanced and more natural-looking:
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): A strip of scalp is removed, and individual follicular units are dissected and transplanted. It leaves a linear scar but is effective for large areas.
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Individual follicles are taken from the donor site and implanted one by one. This leaves tiny dot scars and is less invasive.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Blood is drawn, processed, and injected into the scalp to stimulate hair growth naturally.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Uses laser light to increase blood flow and encourage follicle activity.
Comparing Hair Restoration Methods
Let’s break down the main restoration options in a simple table to help understand which might be best for you:
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Follicular Unit Transplant | Effective for large areas | Leaves linear scar, longer recovery |
| Follicular Unit Extraction | Minimal scarring, natural look | Time-consuming, more expensive |
| PRP Therapy | Non-surgical, promotes growth | Results vary, multiple sessions needed |
| Low-Level Laser Therapy | Painless, easy to use at home | Works best for early hair loss only |
Practical Examples: Choosing the Right Method in New York
Imagine two New Yorkers: John, a 45-year-old man with advanced male pattern baldness, and Sarah, a 30-year-old woman noticing early thinning.
- John might benefit from FUT if he wants a one-time, effective solution and doesn’t mind a scar behind his head.
- Sarah, on the other hand, could try PRP combined with LLLT to boost her natural hair growth without surgery.
This shows how knowing the science behind your hair loss helps in picking the right restoration path. Clinics in New York offer consultations to figure out your hair type, loss pattern, and lifestyle to customize your treatment.
Why Understanding Hair Follicle Biology Matters
Hair follicles are mini organs beneath the skin that produce hair strands. They’re sensitive to hormones, nutrients, and blood supply. When follicles shrink, they produce thinner hair until no hair grows. Restoration treatments aim to revive these follicles or replace them with healthy ones.
- Hair follicles goes through cycles differently depending on genetics and health.
- DHT hormone binds to receptors on follicles causing them to shrink.
- Some follicles are resistant to D
Natural vs. Surgical Hair Restoration: Which Option Delivers Lasting Results According to Science?
Natural vs. Surgical Hair Restoration: Which Option Delivers Lasting Results According to Science?
Hair loss, it’s a struggle many faces, especially men but women too, in New York or anywhere else. People often wonder, what’s the best way to restore hair? Should I try natural methods or go directly for surgical options? Science has been digging deep into this question for years, trying to reveal what really works in the long term. This article dives into the science behind hair restoration, uncovering secrets that might surprise you.
The Science Behind Hair Loss and Restoration
Before talking about restoration, it’s important to understand why hair loss happens. The most common cause is androgenetic alopecia, or male/female pattern baldness. This condition is linked to genetics and hormones, particularly a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT shrinks hair follicles, making hair thinner and eventually stopping growth.
Scientists study hair follicles at microscopic level, finding out how they cycle through growth phases:
- Anagen: Active growth phase lasting 2-6 years
- Catagen: Transitional phase lasting 2-3 weeks
- Telogen: Resting phase lasting 2-3 months
Hair restoration tries to extend anagen or reactivate dormant follicles.
Natural Hair Restoration: What’s It All About?
Natural hair restoration involves methods that don’t require surgery or invasive procedures. These could be topical treatments, lifestyle changes, or supplements. Some popular natural approaches include:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): A topical solution that widens blood vessels, increasing blood flow to hair follicles.
- Biotin and other vitamins: Thought to strengthen hair, though scientific evidence varies.
- Scalp massage: Believed to stimulate circulation and hair growth.
- Essential oils (like rosemary oil): Some studies suggest they may promote hair thickness.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy: Using your own blood to inject growth factors into scalp.
While natural methods sound appealing because they’re less risky, their effectiveness varies. Minoxidil, for example, can slow hair loss but usually doesn’t fully restore lost hair. Vitamins help if deficiencies exist but won’t reverse genetic baldness.
Surgical Hair Restoration: A More Direct Approach
Surgical hair restoration is about physically relocating hair follicles from one area of scalp to another. The two main techniques are:
- FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): A strip of scalp is removed, dissected into grafts, and implanted.
- FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Individual follicles are extracted and transplanted.
These procedures have been around since the 1950s but refined drastically over years. Modern FUE offers less scarring and quicker recovery.
Surgical restoration offers permanent results because transplanted follicles are resistant to DHT. But it’s not magic – success depends on surgeon’s skill, patient’s health, and realistic expectations.
Comparing Natural vs Surgical Hair Restoration: A Quick Look
| Aspect | Natural Hair Restoration | Surgical Hair Restoration |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Invasive (minor surgery) |
| Recovery Time | None or minimal | Days to weeks |
| Effectiveness | Varies, mostly slows hair loss | Permanent, restores hair density |
| Cost | Generally affordable | More expensive |
| Risks | Few side effects (skin irritation, etc.) | Infection, scarring, graft failure |
| Time to See Results | Months | Months to a year |
| Maintenance | Continuous use required | Usually no ongoing treatment needed |
What Does Science Say About Lasting Results?
Scientific studies have shown that surgical hair transplantation tends to deliver more lasting and noticeable results compared to natural methods. Because transplanted hair follicles come from areas resistant to hormone effects, they continue growing for decades.
Natural treatments like minoxidil and finasteride (a prescription drug) can slow or stop hair loss but require lifelong use. Stop using them and hair loss likely returns. PRP therapy shows promise but needs more large-scale studies.
One interesting fact: combining approaches may boost results. For example, some patients use minoxidil after surgery to promote healing and maximize growth.
Practical Examples From Real Life
John, a 35-year-old New Yorker, tried natural remedies for 3 years — vitamins, essential oils, and minoxidil. His hair loss slowed but didn’t reverse. Frustrated, he opted for FUE transplant. After 9 months, his hair looks fuller and natural.
Maria, 42, prefers avoiding surgery. She uses minoxidil and does scalp massages daily. Her hair loss stabilized, but she still has thinning areas. She considers PRP next.
Historical Context: How
Conclusion
In summary, the science behind hair restoration is a fascinating blend of biology, technology, and innovative medical treatments aimed at combating hair loss effectively. From understanding the hair growth cycle and the causes of hair thinning to exploring advanced techniques such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, hair transplant procedures, and emerging stem cell research, each approach offers unique benefits tailored to individual needs. The integration of these scientific advancements has significantly improved success rates and patient satisfaction, providing hope for those struggling with hair loss. As research continues to evolve, it’s essential to consult with qualified professionals to determine the most suitable treatment options based on your specific condition. If you’re considering hair restoration, take the first step today by seeking expert advice and exploring the latest scientifically backed solutions to regain not only your hair but also your confidence.